Top Stories
New Study: Music Cuts Dementia Risk by Nearly 40% for Seniors
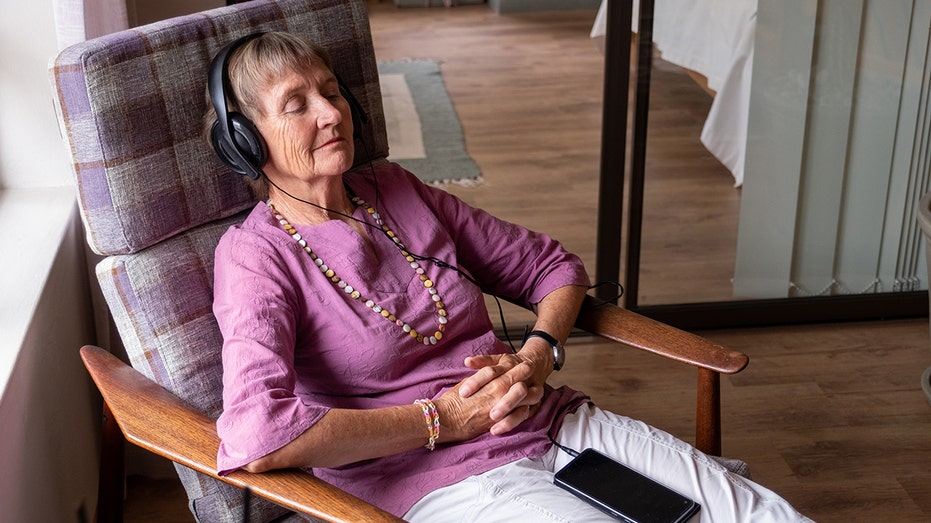

URGENT UPDATE: A groundbreaking study reveals that listening to music could reduce the risk of dementia by nearly 40% for adults over 70. Conducted by researchers at Monash University in Melbourne, Australia, this finding highlights a significant lifestyle choice that can impact cognitive health.
The study shows that seniors who regularly listen to music have a 39% lower likelihood of developing dementia, while those who play instruments enjoy a 35% lower risk. The combined effects of both activities provide even greater protection against cognitive decline.
Researchers tracked over 10,800 adults aged 70 and older for several years, assessing their music engagement through a comprehensive survey. The results, published in the International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, underscore the potential of music as a simple yet powerful strategy for maintaining cognitive function.
“With no cure currently available for dementia, identifying strategies to help prevent or delay onset is critical,” stated Professor Joanne Ryan, a lead researcher on the study. “Brain aging is influenced not just by age and genetics, but also by environmental and lifestyle choices.”
Additionally, the research indicates that regular music engagement can lower the risk of mild cognitive impairment by 22%, leading to improved overall cognition and episodic memory—key components for recalling daily events.
The study highlights that musical activities may be particularly beneficial for older adults with higher educational backgrounds, suggesting a correlation between education level and the protective effects of music.
While the findings are promising, experts caution that causation has not been definitively established. Dr. Morten Scheibye-Knudsen from the University of Copenhagen emphasizes the importance of mental stimulation, but notes that research outcomes in this area remain mixed. He adds, “There are additional benefits to playing an instrument, including increased social interactions, which are vital as we age.”
With dementia affecting approximately 57 million people globally, the implications of this research are profound. As the world grapples with an aging population, music could emerge as an accessible method for enhancing cognitive health among older adults.
This study adds to growing evidence that engaging in creative, social, and mentally stimulating hobbies—such as music, reading, and art—can bolster brain health in later life.
WHAT’S NEXT: As the research community continues to explore the links between music and cognitive health, seniors and caregivers are encouraged to incorporate music into daily routines. The broader implications of these findings could pave the way for new preventive strategies against dementia, offering hope to millions.
Stay tuned for more updates as this research evolves and more studies enter the field.
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Joins $25.6M AI Initiative to Monitor Disasters
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoToledo City League Announces Hall of Fame Inductees for 2024
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoDOJ Seizes $15 Billion in Bitcoin from Major Crypto Fraud Network
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoSharp Launches Five New Aquos QLED 4K Ultra HD Smart TVs
-

 Sports2 months ago
Sports2 months agoCeltics Coach Joe Mazzulla Dominates Local Media in Scrimmage
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoMutual Advisors LLC Increases Stake in SPDR Portfolio ETF
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoCommunity Unites for 7th Annual Walk to Raise Mental Health Awareness
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoWestern Executives Confront Harsh Realities of China’s Manufacturing Edge
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoINK Entertainment Launches Exclusive Sofia Pop-Up at Virgin Hotels
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoMajor Networks Reject Pentagon’s New Reporting Guidelines
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoAstronomers Discover Twin Cosmic Rings Dwarfing Galaxies
-

 Top Stories1 month ago
Top Stories1 month agoRandi Mahomes Launches Game Day Clothing Line with Chiefs