Science
Mitochondria Shift Towards Cell Membrane in Response to Glucose
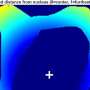
Research published in the Biophysical Journal reveals that mitochondria, the energy-producing organelles within cells, move toward the cell membrane when exposed to elevated glucose levels. This finding is particularly significant in the context of beta cells, which are responsible for producing insulin in the pancreas. Understanding how and why these organelles migrate is crucial for advancing knowledge in diabetes and cellular metabolism.
Mitochondria are not static; they can relocate within cells based on various stimuli. This new study highlights a specific response to high glucose concentrations, which is relevant for individuals with diabetes, where glucose regulation is impaired. The research indicates that as glucose levels rise, beta cells exhibit a pronounced shift in mitochondrial positioning.
Insights into Cellular Dynamics
The migration of mitochondria to the cell periphery suggests a potential mechanism through which beta cells may enhance their insulin secretion capabilities. By positioning themselves closer to the cell membrane, mitochondria could facilitate a more efficient release of insulin in response to increased glucose levels. This may represent an adaptive response to ensure that energy production aligns with the cell’s functional requirements.
The researchers conducted experiments that monitored mitochondrial movement in beta cells under controlled conditions. They observed that the organelles were not only migrating toward the cell membrane but also undergoing structural changes to optimize their function. This dynamic behavior underscores the complexity of cellular responses to metabolic signals.
Understanding these processes could pave the way for innovative therapies targeting mitochondrial function in diabetes management. As the global prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, insights into cellular mechanisms such as these are vital for developing new treatment strategies.
Implications for Diabetes Research
The implications of this study extend beyond basic biology; they could influence therapeutic approaches for metabolic disorders. By clarifying the relationship between glucose levels and mitochondrial dynamics, researchers can better comprehend how beta cells operate under stress, such as during prolonged high glucose exposure.
This research not only contributes to the existing body of knowledge about cellular physiology but also opens avenues for further investigation into the role of mitochondria in other cell types and conditions. Exploring these relationships is essential for developing comprehensive strategies to combat diabetes and related metabolic diseases.
In conclusion, the movement of mitochondria toward the cell membrane in response to high glucose levels highlights the intricate relationship between cellular energy management and insulin secretion. As researchers continue to uncover these mechanisms, the potential for targeted therapies in diabetes becomes increasingly promising.
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Joins $25.6M AI Initiative to Monitor Disasters
-
 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoInterstellar Object 3I/ATLAS Emits Unprecedented Metal Alloy
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoToledo City League Announces Hall of Fame Inductees for 2024
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoDOJ Seizes $15 Billion in Bitcoin from Major Crypto Fraud Network
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoWestern Executives Confront Harsh Realities of China’s Manufacturing Edge
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoSharp Launches Five New Aquos QLED 4K Ultra HD Smart TVs
-

 Politics3 months ago
Politics3 months agoMutual Advisors LLC Increases Stake in SPDR Portfolio ETF
-

 Sports3 months ago
Sports3 months agoCeltics Coach Joe Mazzulla Dominates Local Media in Scrimmage
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoCommunity Unites for 7th Annual Walk to Raise Mental Health Awareness
-

 Politics3 months ago
Politics3 months agoMajor Networks Reject Pentagon’s New Reporting Guidelines
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoINK Entertainment Launches Exclusive Sofia Pop-Up at Virgin Hotels
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoMicrosoft Releases Urgent Windows 11 25H2 Update for All Users









