Science
T. rex Growth Study Reveals Slow Maturation Until Age 40
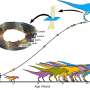
A recent study has challenged long-held beliefs about the growth rate of the Tyrannosaurus rex, indicating that these formidable predators continued to grow until they reached the age of 40. This research, conducted by a team at the University of California, Berkeley, utilized advanced techniques to analyze the fossilized leg bones of T. rex, revealing a more gradual maturation process than previously understood.
For decades, scientists have employed a method akin to counting tree rings, examining annual growth rings within the bones to estimate the ages and growth patterns of these ancient creatures. Until now, the prevailing consensus was that T. rex typically ceased growing around the age of 25. This new finding significantly extends that timeline, providing fresh insights into the life cycle of one of the most iconic dinosaurs.
New Insights from Fossil Analysis
The research focused on the leg bones of several T. rex specimens, with scientists meticulously counting the growth rings to determine the age at which each dinosaur died. The findings revealed that the growth rate was notably slower and more prolonged, suggesting that these dinosaurs continued to grow for up to 15 additional years beyond previous estimates.
By examining the bones of T. rex specimens dating back to the 1990s, the researchers were able to identify distinct patterns in the growth rings. This method provides a clearer understanding of not just how long T. rex lived but also how it adapted to its environment as it matured.
The study’s lead author, Dr. Mark G. McKinley, emphasized the implications of their findings: “Understanding the growth patterns of T. rex helps us to better appreciate the biological and ecological dynamics of these creatures during the Late Cretaceous period.”
Implications for Dinosaur Research
The implications of this research extend beyond T. rex. By establishing a clearer timeline for the growth of these dinosaurs, scientists can develop more accurate models of their behavior, reproductive strategies, and interactions with other species in their ecosystems.
Furthermore, the discovery that T. rex continued to grow into its later years may inform discussions about the evolutionary adaptations of large predators. This could lead to a reevaluation of assumptions regarding the life history traits of other dinosaur species and their growth patterns.
As paleontologists continue to investigate the lives of dinosaurs through fossil analysis, this study stands as a significant milestone. It not only enhances our understanding of the king of dinosaurs but also sets the stage for future research that may uncover more about the biology of these magnificent creatures.
With each new discovery, the narrative of the dinosaurs becomes richer and more complex, reminding us that even the most well-known species can hold surprising secrets waiting to be uncovered.
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Joins $25.6M AI Initiative to Monitor Disasters
-
 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoInterstellar Object 3I/ATLAS Emits Unprecedented Metal Alloy
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoToledo City League Announces Hall of Fame Inductees for 2024
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoDOJ Seizes $15 Billion in Bitcoin from Major Crypto Fraud Network
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoWestern Executives Confront Harsh Realities of China’s Manufacturing Edge
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoSharp Launches Five New Aquos QLED 4K Ultra HD Smart TVs
-

 Politics3 months ago
Politics3 months agoMutual Advisors LLC Increases Stake in SPDR Portfolio ETF
-

 Sports3 months ago
Sports3 months agoCeltics Coach Joe Mazzulla Dominates Local Media in Scrimmage
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoCommunity Unites for 7th Annual Walk to Raise Mental Health Awareness
-

 Politics3 months ago
Politics3 months agoMajor Networks Reject Pentagon’s New Reporting Guidelines
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoINK Entertainment Launches Exclusive Sofia Pop-Up at Virgin Hotels
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoMicrosoft Releases Urgent Windows 11 25H2 Update for All Users









